Course Glossary
This shows the specialized terms used in EarthWise Academy. This section contains all the definitions used in the various course glossaries used by each course.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
Entries starting with: M |
|---|
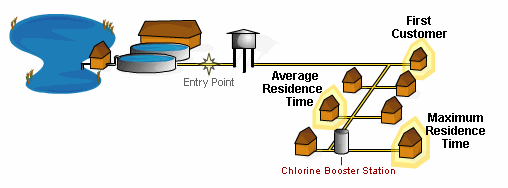
M SampleSample collected from the location in the distribution system with the maximum residence time.
|
M/DBPM/DBP – Microbial/Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproduct
|
M/RMonitoring and Reporting
|
Mandatory Health Effects LanguageSpecific health effects language required for primary MCL or MRDL violation, treatment technique violations and violation of the condition of a variance or exemption.
|
Maximum Contaminant Level
|
Maximum Contaminant Level GoalMaximum Contaminant Level Goal (MCLG) The level of a contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MCLGs allow for a margin of safety.
|
Maximum ResidenceThat area of the distribution system where the water has the longest standing time and the longest contact time with a chemical disinfectant.
|
Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level
|
MCL
|
MCLGMCLG – Maximum Contaminant Level Goal The level of a contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MCLGs allow for a margin of safety.
|
MCRTMCRT - Mean Cell Residence Time An expression of the average time that a microorganism or solid particle undergoes aeration in the activated sludge process.
|
Mean Cell Residence TimeMean Cell Residence Time (MCRT) An expression of the average time that a microorganism or solid particle undergoes aeration in the activated sludge process.
|
MethemoglobinemiaBlood disorder caused when nitrite, converted from nitrate in the digestive system, interacts with the hemoglobin in red blood cells forming methemoglobin which cannot carry sufficient oxygen to the body's cells and tissues.
|
MGDMillion Gallons per Day
|
Microbial/Disinfectants and Disinfection ByproductMicrobial/Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproduct – (M/DBP)
|
Microflocs
|
Million Gallons per DayMillion Gallons per Day – MGD
|
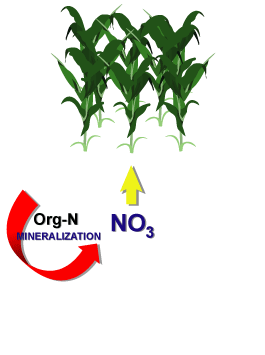
MineralizationThe conversion of an element from an organic form to an inorganic state as a result of microbial activity.
|
Mixed Liquor Suspended SolidsMixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS) The concentration of suspended solids (both organic and inorganic) in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank. MLSS is used as a measure of the concentration of microorganisms present.
|
Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS)The concentration of suspended solids (both organic and inorganic) in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank. MLSS is used as a measure of the concentration of microorganisms present.
|
MLSSMLSS – Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids The concentration of suspended solids (both organic and inorganic) in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank. MLSS is used as a measure of the concentration of microorganisms present. |
MLSS – Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS)The concentration of suspended solids (both organic and inorganic) in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank. MLSS is used as a measure of the concentration of microorganisms present.
|
Monitoring and Reporting ViolationAny violation incurred for failing to monitor and/or report for a regulated parameter specified by the Pa. DEP.
|
Monitoring PeriodThe time frame, generally in months, quarters, or years, during which water samples must be collected and tested in accordance with Pa Safe Drinking Water Regulations to determine compliance with applicable MCLs, MRDLs, or treatment techniques
|
MRDL
|
MRDLGMRDLG – Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level Goal The unenforceable maximum level of disinfectant added for water treatment for which there is no known risk to human health.
|
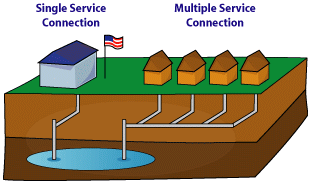
Multiple Service ConnectionThis refers to the condition where a PWS serves many individual buildings (connections), i.e., homes or businesses that use public water.
|