90th Percentile Tap Sample ResultIdentification of the 90th percentile tap sample result is accomplished by following two steps:
|
ACCACC - Alternative Compliance Criteria
Alternative criteria that can be used to achieve either monthly or annual compliance with the enhanced coagulation requirements of the DBP Rule.
|
AcidicA condition in which a substance yields H+ ions when it dissociates in water, resulting in a lowering of pH.
|
AcidityThe concentration of H+ ions in a solution, measured as pH.
|
Action Level
|
Activated SilicaA coagulant aid that is created on-site by neutralizing sodium silicate.
|
Activated Sludge ProcessA biological treatment process in which a mixture of wastewater and activated sludge is agitated and aerated. The activated sludge is subsequently separated from the treated wastewater by settlement and recycled or wasted. Although the configuration of activated sludge plants vary, the activated sludge process includes one or more aerated reactors that keep the solids in suspension; a liquid-solids separation device known as a clarifier; and a method of recycling the separated sludge from the clarifier back to the aerated reactor(s).
|
Acute health effectsAdverse effect on human health as a result of short-term exposure. Acute health effects occur within hours or days of the time that a person consumes a contaminant.
|
Additional Routine Monitoring
|
AdsorbThe accumulation of one material on the surface of another material through physical bonds
|
AdsorptionThe gathering of a gas, liquid, or dissolved substance at the surface at the surface of solid bodies with which they are in contact.
|
Advanced TreatmentConsists of additional biological or chemical treatment processes (beyond secondary treatment) that are employed to remove constituents such as nitrogen and phosphorus, that are not reduced significantly as a result of secondary treatment. Any process of water renovation that upgrades treated wastewater to meet specific reuse requirements. May include general cleanup of water or removal of specific parts or wastes insufficiently removed by conventional treatment processes. Typical processes include chemical treatment and pressure filtration.
|
AerobicA condition in which high levels of dissolved oxygen are made available.
|
Aerobic BacteriaAlso called aerobes
Bacteria that must have molecular (dissolved) oxygen to survive. Bacteria that will live and reproduce only in an environment containing oxygen, which is available for their respiration (breathing), namely atmospheric oxygen or oxygen dissolved in water. Oxygen combined chemically, such as in water molecules (H2O), cannot be used for respiration by aerobic bacteria.
|
Agronomic Loading RatesThe annual whole biosolids application rate designed to:
|
AL
|
Alkaline(DBP40) Enhanced Coagulation – Basics (1280) |
Alkalinity
|
Alternative Compliance CriteriaAlternative Compliance Criteria (ACC)—
Alternative criteria that can be used to achieve either monthly or annual compliance with the enhanced coagulation requirements of the DBP Rule. |
AnaerobicA condition in which dissolved molecular oxygen is not present, however, some chemically bound oxygen may be present.
|
Anaerobic BacteriaAlso known as anaerobes.
Bacteria that live and reproduce in an environment containing no "free" oxygen or DO (this type of environment is referred to as anoxic conditions). Anaerobic bacteria obtain their oxygen supply by breaking down chemical compounds which contain oxygen, such as sulfate.
|
AnoxicA condition in which dissolved (atmospheric) oxygen is deficient, however, oxygen is available in the combined form (e.g., nitrate, sulfate and carbonate).
|
Autotrophic OrganismsAlso known as autotrophs.
Organisms that use inorganic materials for energy and growth.
|
AutotrophsOrganisms that use inorganic materials for energy and growth.
|
BasicityThe concentration of OH- ions in a solution, measured as pH or, alternatively, pOH. A solution is basic if it has a pH higher than 7.0 or a pH lower than 7.0.
|
Biochemical Oxygen DemandBiochemical Oxygen Demand — BOD
A measure of the oxygen required to break down organic materials in water using biological means. The amount of oxygen required to oxidize any organic matter present in water during a specified period of time, usually 5 days. It is an indirect measure of the amount of organic matter present in water that is used to monitor natural waters and processed effluents discharged into natural waters.
|
Biological TreatmentMicrorganisms growing and reproducing in a controlled environment are used to partially stabilize (oxidize) organic matter.
|
BiosolidsNutrient-rich organic material that are produced from the stabilization of sewage sludge and residential septage that meets specific quality criteria and are suitable for land application.
|
Biosolids (Exceptional Quality)Biosolids that meet stricter pollutant and pathogen reduction criteria.
|
Biosolids (Non-Exceptional Quality)Non-exceptional quality biosolids are biosolids that meet specified pollutant and pathogen reduction criteria. Criteria for non-exceptional quality biosolids are less stringent than criteria for exceptional quality biosolids. Note: The term 'Biosolids' can be used to refer to all categories of biosolids collectively, or can be used to refer specifically to the category non-exceptional quality biosolids.
|
BODBOD — Biochemical Oxygen Demand A measure of the oxygen required to break down organic materials in water using biological means. The amount of oxygen required to oxidize any organic matter present in water during a specified period of time, usually 5 days. It is an indirect measure of the amount of organic matter present in water that is used to monitor natural waters and processed effluents discharged into natural waters.
|
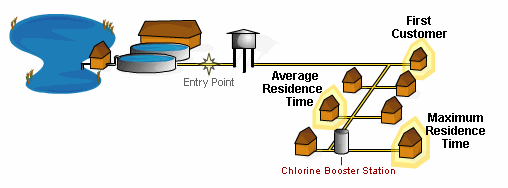
Booster ChlorinationWater is treated with an additional boost of chlorine from within the distribution system.
|
Bottled Water SystemA public water system that provides water for bottling in sealed bottles or other sealed containers. The term includes, but is not limited to, the sources of water and treatment, storage, bottling, manufacturing and distribution facilities. The term does not include a public water system that provides only a source of water supply for a bottled water system and excludes an entity providing only transportation, distribution or sale of bottled water in sealed bottles or other sealed containers.
|
Bottled, Vended, Retail, & Bulk-delivered Water SystemsBottled, Vended, Retail, & Bulk-delivered Water Systems – (BVRB)
|
Buffering CapacityThe ability of a solution to neutralize acids without a significant change in pH. Buffering capacity is also known as alkalinity and is measured in mg/L of equivalent CaCO3, a common buffer. |
Bulk Water-Hauling SystemA public water system that provides water piped into a carrier vehicle and withdrawn by a similar means into the user's storage facility or vessel. The term includes, but is not limited to, the source of water, treatment, storage or distribution facilities. The term does not include a public water system that provides only a source of water supply for a bulk water hauling system.
|
BVRBBVRB - Bottled, Vended, Retail, & Bulk-delivered water systems
|
Ca(OH)2Ca(OH)2
|
Calcium hydroxideCa(OH)2
|
Capital Improvements PlanningA process for considering the future purchase or construction of expensive items.
|
Carbonaceous BOD (cBOD)The stage of decomposition that occurs in biological treatment processes when aerobic bacteria, using DO, change carbon compounds to carbon dioxide; cBOD is sometimes referred to as "first-stage BOD" because the microorganisms attack organic or carbon compounds first. (Nitrogen compounds are targeted second, sometimes referred to as nBOD or "second stage BOD.")
|
Carbonate SystemMajor acid/base system that produces a chemical reaction in water distribution systems. The carbonate system is comprised of:
|
CationicAn ion with a positive charge.
|
cBODcBOD (Carbonaceous BOD) The stage of decomposition that occurs in biological treatment processes when aerobic bacteria, using DO, change carbon compounds to carbon dioxide; cBOD is sometimes referred to as "first-stage BOD" because the microorganisms attack organic or carbon compounds first. (Nitrogen compounds are targeted second, sometimes referred to as nBOD or "second stage BOD.")
|
CCRCCR -Consumer Confidence Report An annual water quality report that community water systems deliver to their customers.
|
CCTCCT - Corrosion Control Treatment Water treatment that minimizes the lead and copper concentrations at users' taps while ensuring that the treatment does not cause the system to violate any primary maximum contaminant level.
|
Critical AssetComponents of a water or waste water treatment system that are necessary to meet mission objectives (providing drinking water that meets or exceeds the National Drinking Water Standards, providing adequate water pressure to meet public safety needs, maintaining water service to critical users, maintaining wastewater collection system to protect public health, and providing wastewater treatment that meets the National Pollution Discharge Elimination System standards.
|
CWSCWS - Community Water System
|
D SampleSample collected from the distribution system.
|
D Sampling SitesRepresentative sites within the distribution system.
|
DBP Rule
DBP Rule - Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule
|
DBPs
|
DBTDBT - Design Basis Threat Description of a specific adversary and mode of attack that has a degree of likelihood of occurring.
|
DenitrificationAn anoxic process that occurs when nitrite or nitrate ions are reduced to nitrogen gas and nitrogen bubbles are formed as a result of this process.
|
DenitrifiersFacultative heterotrophic bacteria (such as Pseudomonas, Bacillus and Achromobacter) that convert nitrate in wastewater to nitrogen gas, given an anoxic environment.
|
Denitrifying bacteriaAlso known as denitrifiers. Specialized bacteria (such as Pseudomonas and Achromobacter) that convert nitrate in wastewater, into nitrogen gas.
|
DEPDEP - Department of Environmental Protection
|
Department of Environmental ProtectionDepartment of Environmental Protection (DEP)
|
Design Basis ThreatDesign Basis Threat (DBT) Description of a specific adversary and mode of attack that has a degree of likelihood of occurring.
|
DestabilizedA condition in which the electrical charge of particles has been neutralized.
|
Detected ContaminantAny contaminant detected at or above its detection limit.
|
Detection LimitThe amount of a substance with that EPA has determined to be the minimum concentration that can be measured and reported with 99% confidence that the true value is greater than zero.
|
Detention TimeThe theoretical time that a parcel of water or other liquid spends in a particular treatment unit or reservoir.
|
Diatomaceous EarthA fine material made up mostly of the skeletal remains of single cell, microscopic algae with a rigid, box-like internal structure consisting mainly of silica.
|
Digester CapacityThe total volume in gallons that a digester(s) can hold, or the volume used during the monitoring period, if not operating at full capacity.
|
Discharge Monitoring ReportDischarge Monitoring Report (DMR) |
DisinfectantsSubstances that are added for the purpose of killing or inactivating the pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria found in water.
|
Disinfection Byproducts PrecursorsOrganic substances that combine with disinfectants to form potentially carcinogenic compounds such as HAA5’s and TTHM’s.
|
Dissolved OxygenDissolved Oxygen (DO) A measure of the amount of free or molecular oxygen dissolved in water, expressed as:
|
DMRDMR – Discharge Monitoring Report
|
DODO - Dissolved Oxygien
|
Double Layer CompressionIn the double layer compression mechanism large quantities of a salt that has no charge (neutral) are added. The salt works by compressing the double layer around the colloid. When the outer layer is compressed, the repulsive energy barrier around the colloid is reduced or eliminated. This allows the particles to combine.
|
Drinking Water Electronic Laboratory ReportingDrinking Water Electronic Laboratory Reporting (DWELR) A web-based application that provides a means for laboratories that are accredited by or registered with DEP’s Bureau of Laboratories to submit their drinking water sample data to DEP’s public drinking water program.
|
DWELRDWELR - Drinking Water Electronic Laboratory Reporting A web-based application that provides a means for laboratories that are accredited by or registered with DEP’s Bureau of Laboratories to submit their drinking water sample data to DEP’s public drinking water program.
|
ERPERP - Emergency Response Plan Contains policies, authorities, concept of operations, legal constraints, responsibilities, and emergency functions to be performed. Agency response plans, responder SOPs and specific incident action plans are developed from this strategic document.
|
Exceptional Quality BiosolidsBiosolids that meet stricter pollutant and pathogen reduction criteria.
|
Facultative BacteriaBacteria that can use either dissolved oxygen or chemically derived oxygen (from nitrate, sulfate or carbonate) for respiration and use organic materials for energy and growth. In other words, facultative heterotrophs can live under aerobic, anoxic or anaerobic conditions.
|
Fecal Coliform BacteriaColiform bacteria (microorganisms) found in the intestinal tract of warm-blooded animals (including humans). Unlike total coliforms, which include a number of normal soil inhabitants that are harmless, fecal coliforms are more reliable indicators of fecal contamination, which may result in the spread of intestinal disease.
|
Federal Safe Drinking Water ActThe Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) was established to protect the quality of drinking water in the U.S. This law focuses on all waters actually or potentially designed for drinking use, whether from aboveground or underground sources. The Act authorized EPA to establish safe standards of purity and required all owners or operators of public water systems to comply with primary (health-related) standards. State governments, which assume this power from EPA, also encourage attainment of secondary standards (aesthetic-related).
|
Field OrderAn appealable notice given when, upon inspection, DEP staff determines a regulated facility has not attempted to correct a violation. These provide the facility with a time frame in which to correct the problem considered to be an imminent threat to human health and environment.
|
FiltrateLiquid derived from the dewatering of sludge.
|
FiltrationThe process of removing fine particles from water by passing the water through various layers of media.
|
Finished WaterWater that has been treated and is ready to be delivered to customers.
|
FlocMasses of non-settleable microorganisms and particles that come together to form progressively larger, heavier particles. |
Flow RateRate of wastewater flow through a wastewater treatment facility, typically measured in million gallons per day (MGD).
|
ForageHerbage that is available and acceptable to grazing animals.
|
FrequencyHow often sampling occurs.
|
General PermitA statewide permit issued by the Department for a specific category of beneficial use, such as the beneficial use of biosolids, that a person or municipality that obtains a determination of applicability to operate under the permit if the terms and conditions of the permit and certain requirements are met
|
Grandfatheralso grandfathering Use of historical data to determine if initial monitoring can be skipped.
|
Green ManureCover crop that is incorporated into the soil, while green, for soil improvement.
|
Ground WaterGround Water (GW)
|
Ground Water Under the Direct Influence of Surface WaterGround Water Under the Direct Influence of Surface Water (GUDI)
|
GUDIGUDI – Ground Water Under the Direct Influence of Surface Water
|
HeadworksThe facilities where wastewater enters a wastewater treatment plant.(BNR01) Nitrification and Denitrification – An Introduction to Nitrogen Removal (1485)
|
Heterotrophic OrganismsOrganisms that use organic materials for energy and growth.
|
HeterotrophsOrganisms that use organic materials for energy and growth.
|
ICRICR – Information Collection Rule
|
IESWTRIESWTR – Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule
|
Imminent Threat ViolationA condition at a PWS that may adversely affect the quality of drinking water and presents an immediate threat to public health.
|
Incomplete DenitrificationA condition in which environmental conditions are not optimal to provide for the conversion of nitrate to nitrogen gas (some of the nitrate remains as nitrate and some undergoes partial conversion yielding concentrations of nitrite). Typically, incomplete denitrification results in high levels of nitrate in the wastewater effluent.
|
Incomplete NitrificationA condition in which not all ammonia is converted to nitrate (some of the ammonia remains as ammonia and some of the ammonia undergoes partial conversion yielding concentrations of nitrite). Typically, incomplete nitrification results in high levels of ammonia in the wastewater effluent.
|
IncorporationMixing of materials found on or spread upon the soil surface into the soil volume via the mechanical manipulation of the soil.
|
InfluentWastewater or other liquid - raw (untreated) or partially treated - flowing INTO a reservoir, basin, treatment process, or treatment plant
|
Information Collection RuleInformation Collection Rule (ICR)
|
InorganicDescribes material that is of mineral origin. Specifically, describes chemical compounds that do not contain carbon and hydrogen.
|
Inorganic MaterialMaterial such as sand, salt, iron, calcium and other mineral materials that are only slightly affected by the action of organisms in wastewater treatment. Inorganic matter is comprised of chemical substances of mineral origin; whereas organic matter is comprised of chemical substances that are usually of animal or plant origin.
|
Inorganic MatterParticles produced by natural weathering of minerals. Examples include sand, salt, iron, calcium salts and other mineral materials.
|
Inorganic WasteWaste material such as sand, salt, iron, calcium and other mineral materials that are only slightly affected by the action of organisms in wastewater treatment. Inorganic wastes are chemical substances of mineral origin; whereas organic wastes are chemical substances usually of animal or plant origin.
|
Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment RuleInterim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule – (IESWTR)
|
Intermittent TCR M/R ViolatorsAny PWS with 3 or less monthly or one quarterly monitoring violation during a 12 month period.
|
IonAn atom or molecule with an electrical charge.
|
IonizationA process causing a movement of electrons within a compound (dissociation of ions) which subsequently causes metals to dissolve.
|
Jar TestingLaboratory, bench-scale tests designed to simulate the water plant's coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation processes. The tests can be used to experiment with such things as different coagulants, polymers, and pH ranges.
|
Land ApplicationThe spraying or spreading of biosolids onto the land surface, the injection of biosolids below the land surface or the incorporation of biosolids into the soil for beneficial use so that the biosolids can either condition the soil or fertilize crops or vegetation grown in the soil.
|
Land Reclamation SiteDrastically disturbed land that is reclaimed using biosolids. The term includes, but is not limited to, active and abandoned coal and noncoal surface mines and construction sites.
|
LCRLCR - Lead and Copper Rule
|
LeachingTo dissolve out by the action of a percolating liquid.
|
Lead and Copper RuleLead and Copper Rule (LCR)
|
Lead Service Lines
|
LegumePlant that has formed a symbiotic relationship with bacteria (rhizobia) that have the capability to fix nitrogen (convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for plants) addition, such as soybeans, alfalfa, red clover and trefoil.
|
Levels for Reduced TTHM/HAA5 Monitoring040 mg/L and .030 mg/L for TTHM and HAA5, respectively for all water systems except small GW systems.
|
LimeCaCO3 or CaO - Quick lime. |
LSLs
|
M SampleSample collected from the location in the distribution system with the maximum residence time.
|
M/DBPM/DBP – Microbial/Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproduct
|
M/RMonitoring and Reporting
|
Mandatory Health Effects LanguageSpecific health effects language required for primary MCL or MRDL violation, treatment technique violations and violation of the condition of a variance or exemption.
|
Maximum Contaminant Level
|
Maximum Contaminant Level GoalMaximum Contaminant Level Goal (MCLG) The level of a contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MCLGs allow for a margin of safety.
|
Maximum ResidenceThat area of the distribution system where the water has the longest standing time and the longest contact time with a chemical disinfectant.
|
Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level
|
MCL
|
MCLGMCLG – Maximum Contaminant Level Goal The level of a contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MCLGs allow for a margin of safety.
|
MCRTMCRT - Mean Cell Residence Time An expression of the average time that a microorganism or solid particle undergoes aeration in the activated sludge process.
|
Mean Cell Residence TimeMean Cell Residence Time (MCRT) An expression of the average time that a microorganism or solid particle undergoes aeration in the activated sludge process.
|
MethemoglobinemiaBlood disorder caused when nitrite, converted from nitrate in the digestive system, interacts with the hemoglobin in red blood cells forming methemoglobin which cannot carry sufficient oxygen to the body's cells and tissues.
|
MGDMillion Gallons per Day
|
Microbial/Disinfectants and Disinfection ByproductMicrobial/Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproduct – (M/DBP)
|
Microflocs
|
Million Gallons per DayMillion Gallons per Day – MGD
|
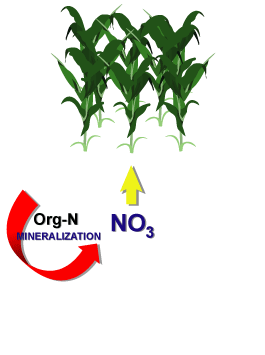
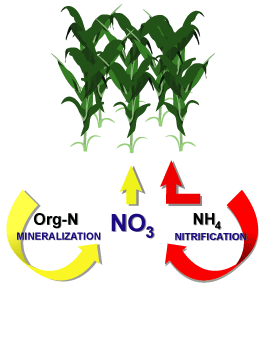
MineralizationThe conversion of an element from an organic form to an inorganic state as a result of microbial activity.
|
Mixed Liquor Suspended SolidsMixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS) The concentration of suspended solids (both organic and inorganic) in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank. MLSS is used as a measure of the concentration of microorganisms present.
|
Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS)The concentration of suspended solids (both organic and inorganic) in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank. MLSS is used as a measure of the concentration of microorganisms present.
|
MLSSMLSS – Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids The concentration of suspended solids (both organic and inorganic) in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank. MLSS is used as a measure of the concentration of microorganisms present. |
MLSS – Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS)The concentration of suspended solids (both organic and inorganic) in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank. MLSS is used as a measure of the concentration of microorganisms present.
|
Monitoring and Reporting ViolationAny violation incurred for failing to monitor and/or report for a regulated parameter specified by the Pa. DEP.
|
Monitoring PeriodThe time frame, generally in months, quarters, or years, during which water samples must be collected and tested in accordance with Pa Safe Drinking Water Regulations to determine compliance with applicable MCLs, MRDLs, or treatment techniques
|
MRDL
|
MRDLGMRDLG – Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level Goal The unenforceable maximum level of disinfectant added for water treatment for which there is no known risk to human health.
|
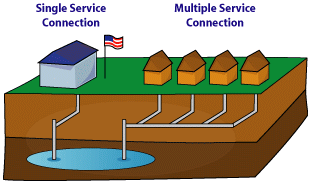
Multiple Service ConnectionThis refers to the condition where a PWS serves many individual buildings (connections), i.e., homes or businesses that use public water.
|
N/A Site
|
National Pollutant Discharge Elimination SystemNational Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES)
|
National Primary Drinking Water RegulationsNational Primary Drinking Water Regulations (NPDWR) NPDWRs (or primary standards) are legally enforceable standards that apply to public water systems.
|
Natural Organic MatterNatural Organic Matter (NOM) - Organic matter that exists naturally in the water environment.
|
Natural RadiologicalsNaturally occurring radiological contaminants including gross alpha, radium-226, radium-228, and uranium.
|
nBODNitrogenous BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) - The stage of decomposition that occurs in biological treatment processes when specialized aerobic bacteria (nitrifiers), use DO to change ammonia to nitrate; sometimes referred to as second-stage BOD.
|
NCWSNCWS - Noncommunity Water System
|
Nitrification
|
NitrifiersSpecialized bacteria (such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter) that change ammonia and organic nitrogen in wastewater, into oxidized nitrogen (usually nitrate).
|
Nitrifying BacteriaAlso known as nitrifiers Specialized bacteria (such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter) that change ammonia and organic nitrogen in wastewater, into oxidized nitrogen (usually nitrate).
|
Nitrogenous BODNitrogenous BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) - The stage of decomposition that occurs in biological treatment processes when specialized aerobic bacteria (nitrifiers), use DO to change ammonia to nitrate; sometimes referred to as second-stage BOD.
|
NOMNOM – Natural Organic Matter
|
Non-Exceptional Quality BiosolidsNon-exceptional quality biosolids are biosolids that meet specified pollutant and pathogen reduction criteria. Criteria for non-exceptional quality biosolids are less stringent than criteria for exceptional quality biosolids. Note: The term 'Biosolids' can be used to refer to all categories of biosolids collectively, or can be used to refer specifically to the category non-exceptional quality biosolids.
|
Noncommunity Water SystemNoncommunity Water System (NCWS)
|
NonsettleableParticles that take a lengthy amount of time to settle by gravity (i.e. many hours, days, or years).
|
Nontransient Noncommunity Water System
|
Notice of ViolationNotice of Violation (NOV)
|
NOVNOV – Notice of Violation
|
NPDESNPDES - National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System
|
NPDWRNPDWR – National Primary Drinking Water Regulations NPDWRs (or primary standards) are legally enforceable standards that apply to public water systems.
|
NTNCWS
|
NucleusA central mass about which other matter collects; a starting point for growth or development.
|
O&MO&M – Operation and Maintenance
|
OCCTOptimal Corrosion Control Treatment - Corrosion control treatment that minimizes the lead and copper concentrations at users' taps while ensuring that the treatment does not cause the system to violate any primary maximum contaminant level.
|
One full yearany 12-consecutive month period of monitoring.
|
Optimal Corrosion Control TreatmentOptimal Corrosion Control Treatment (OCCT) Corrosion control treatment that minimizes the lead and copper concentrations at users' taps while ensuring that the treatment does not cause the system to violate any primary maximum contaminant level.
|
Organic
|
Organic ContaminantsDerived from animals and plants, or may be manufactured chemical compounds. However, all organics contain carbon. Organic contaminants can be biodegradable, which means that the contaminants can be consumed by bacteria and other microorganisms. In the process of being consumed, these organics will exert an oxygen demand (BOD) which can be measured as the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of the wastewater. Some organic contaminants (refractory organics) are resistant to biodegradation.
|
Organic Material
|
Organic SubstancesSubstances that come from animal or plant sources and contain carbon. Examples include wood, sugars, proteins, plastics, petroleum-based compounds, solvents and pesticides.
|
Organic WasteWaste material that comes mainly from animal or plant sources. Organic wastes generally can be consumed by bacteria and other small organisms. Inorganic wastes are chemical substances of mineral origin.
|
Oxidant
|
OxidationThe addition of oxygen, removal of hydrogen, or the removal of electrons from an element of compound. With respect to water treatment, organic matter is oxidized to more stable substances.
|
OzonationThe application of ozone to water for disinfection or for taste and odor control.
|